WHAT ARE THE 4 MAIN TYPES OF VULNERABILITY?
In this modern age a majority of businesses are learning new ways to overcome dire vulnerabilities that can increase the rate of cyber threats. It adversely affect the community’s ability to prevent, mitigate, prepare for or respond to a hazard. Absence of coping strategies is also a part of vulnerability and has to be considered in vulnerability assessment.
WHAT IS VULNERABILITY?
Vulnerability describes the characteristics and circumstances of a community, system or asset that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard. There are many aspects of vulnerability, arising from various physical, social, economic, and environmental factors. Examples may include:
- Poor design and construction of buildings,
- Inadequate protection of assets,
- Lack of public information and awareness,
- Limited official recognition of risks and preparedness measures, and
- Disregard for wise environmental management.
Vulnerability varies significantly within a community and over time. This definition identifies vulnerability as a characteristic of the element of interest (community, system or asset) which is independent of its exposure. However, in common use the word is often used more broadly to include the element’s exposure.
TOP 5 THREAT RISK ASSESSMENT APPROACHES FOR CYBER SECURITY PROFESSIONALS
WHAT CAUSES VULNERABILITIES?
There are many causes of vulnerabilities including:
COMPLEXITY
COMPLEXITY
Complex systems increase the probability of a flaw, misconfiguration or unintended access.
FAMILIARITY

FAMILIARITY
Common code, software, operating systems and hardware increase the probability that an attacker can find or has information about known vulnerabilities.
CONNECTIVITY
CONNECTIVITY
The more connected a device is the higher the chance of a vulnerability.
TOP 10 EMERGING BENEFITS FOR CLOUD BASED MANAGED SERVICES
POOR PASSWORD MANAGEMENT

POOR PASSWORD MANAGEMENT
Weak passwords can be broken with brute force and reusing passwords can result in one data breach becoming many.
OPERATING SYSTEM FLAWS
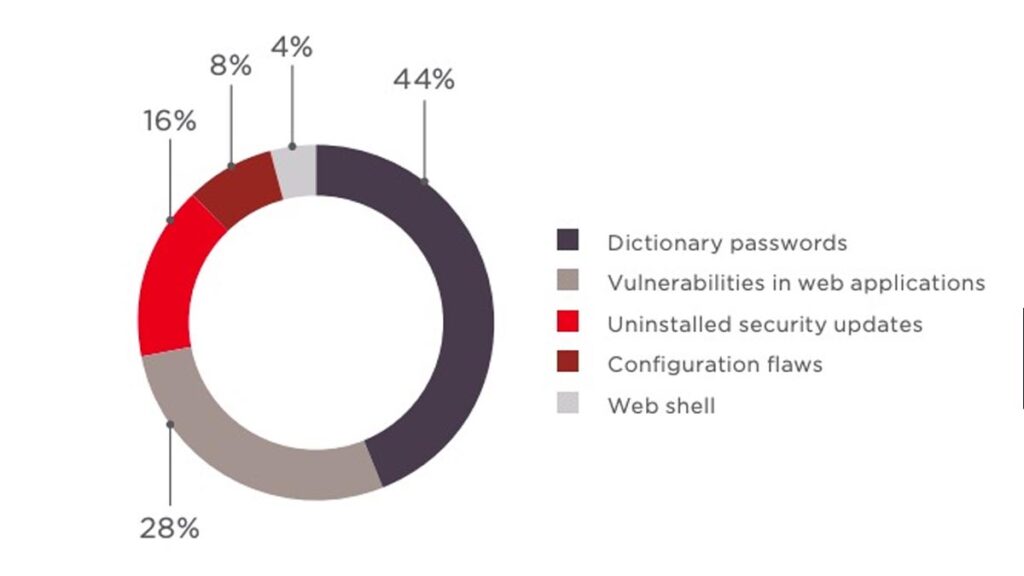
OPERATING SYSTEM FLAWS
Like any software, operating systems can have flaws. Operating systems that are insecure by default and give all users full access can allow viruses and malware to execute commands.
INTERNET USAGE

INTERNET USAGE
The Internet is full of spyware and adware that can be installed automatically on computers.
SOFTWARE BUGS

SOFTWARE BUGS
Programmers can accidentally or deliberately leave an exploitable bug in software.
UNCHECKED USER INPUT
UNCHECKED USER INPUT
If your website or software assume all input is safe it may execute unintended SQL commands.
EMPLOYEES

EMPLOYEES
The biggest vulnerability in any organization is the human at the end of the system. Social engineering is the biggest threat to the majority of organizations.
WHAT IS VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT?
Vulnerability management is a cyclical practice of identifying, classifying, remediating and mitigating security vulnerabilities. The essential elements of vulnerability management include vulnerability detection, vulnerability assessment and remediation. The methods of vulnerability detection include:
- Vulnerability scanning
- Penetration testing
- Google hacking
And once a vulnerability is found, it goes through the vulnerability assessment process.
WHAT ARE THE 4 MAIN TYPES OF VULNERABILITY?
There are four basic and major vulnerabilities:
PHYSICAL VULNERABILITY
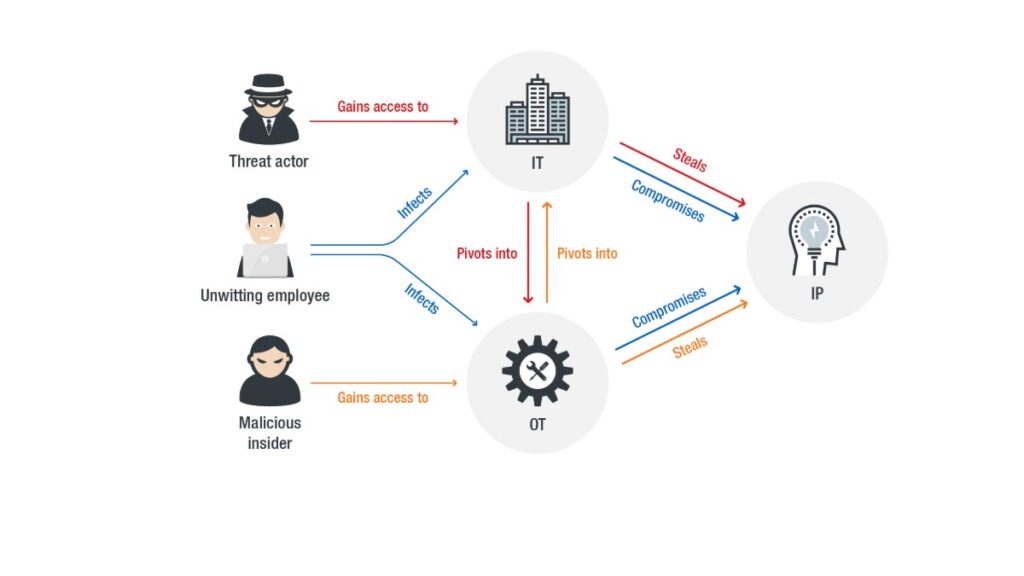
PHYSICAL VULNERABILITY
The physical vulnerability of an area also depends on its geographic proximity to the source and origin of the disasters e.g. if an area lies near the coast lines, fault lines, unstable hills etc. it makes the area more vulnerable to disasters as compared to an area that is far away from the origin of the disaster. Physical vulnerability includes the difficulty in access to water resources, means of communications, hospitals, police stations, fire brigades, roads, bridges and exits of a building or/an area, in case of disasters. Furthermore, the lack of proper planning and implementation in construction of residential and commercial buildings results in buildings that are weaker and vulnerable in earthquakes, floods, landslides and other hazards.
WAYS TO FREE UP SPACE ON YOUR DESKTOP
ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY

ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY
Economic vulnerability of a community can be assessed by determining how varied its sources of income are, the ease of access and control over means of production, adequacy of economic fall back mechanisms and the availability of natural resources in the area.
SOCIAL VULNERABILITY

SOCIAL VULNERABILITY
A socially vulnerable community has weak family structures, lack of leadership for decision making and conflict resolution, unequal participation in decision making, weak or no community organizations, and the one in which people are discriminated on racial, ethnic, linguistic or religious basis. Other social factors such as culture, tradition, religion, local norms and values, economic standard, and political accountability also play a vital role determining the social vulnerability of a community. Social vulnerability to natural phenomena is greatest among the poorest people in developing countries owing to a lack of information and resources with which to take the appropriate measures. Within this group, children, women and the elderly are considered to be the most vulnerable. To reduce social vulnerability, all of the above factors must be addressed but this requires knowledge and understanding of the local conditions, which can in most cases only be provided by local actors.
HOW TO REMOVE TROVI SEARCH FROM THE WEB BROWSER?
ATTITUDINAL VULNERABILITY

ATTITUDINAL VULNERABILITY
A community which has negative attitude towards change and lacks initiative in life resultantly become more and more dependent on external support. They cannot act independently. Their sources of livelihood do not have variety, lacks entrepreneurship and do not possess the concept of collectivism. This brings about disunity and individualism in the society. Thus, they become victims of conflicts, hopelessness and pessimism which reduces their capacity of coping with a disaster. And for more updates you are free to visit Securityx.


0 Comments